Fall 2015 MicroBiped Level 1 Requirements
By Paul Oo
Approved by Paul Oo (Project Manager)
Approved by Michael Balagtas (PCB Design and Manufacturing)
Objective
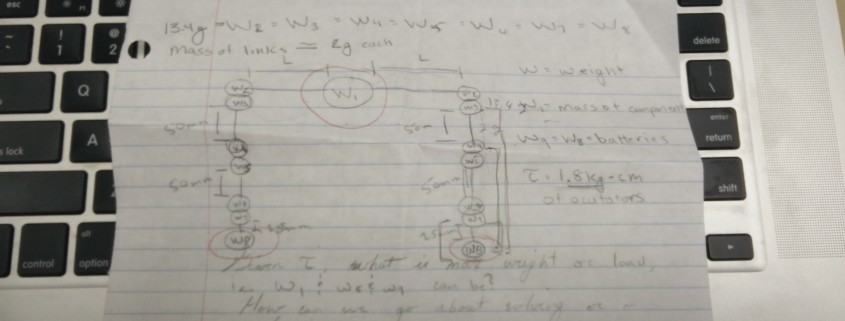
The CSULB μBiped project provides its members with the opportunity to not only design and produce a control theory project, but also to define a purpose for this project. A Biped Robot is designed to model the movement of the human lower body. The goal of this project is to prototype a μBiped that resembles a toy raptor. By customer’s request, this μBiped shall be controlled by Bluetooth on an Android phone. Due to an evolving objective, the payloads shall be determined by the customer.
Level 1 Requirements
Program Requirements:
In order to meet logistical expectations, the following program requirements have been set:
- According to the CSULB Fall 2014 Academic Calendar, the μBiped robot shall be tested by December 16, 2015; the date of the last day of finals.
- The μBiped shall be able to successfully navigate a course with obstacles, inclined path of up to 6o, and varying surfaces.
- According to 2014-2015 ARXTERRA µBiPed’s parts list, the project shall cost no more than $400.00.
Project Requirements:
In order to meet our objective to construct a robot that models human legs, the following project requirements have been set:
- In accordance with the project name, the μBiped shall travel on 2 legs.
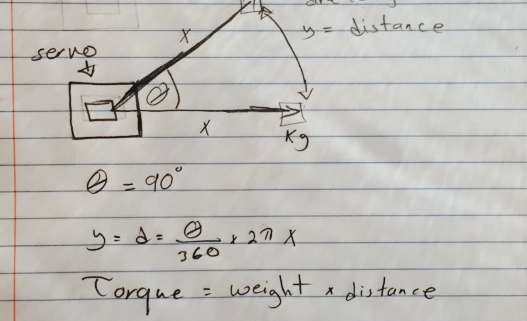
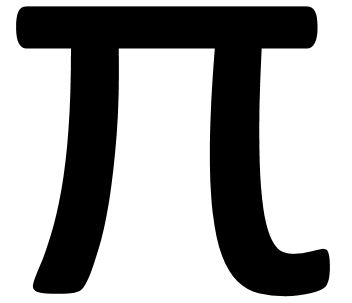
- To be considered a miniaturized Biped robot, the μBiped shall range between ½ (120 mm) ±10% of Rofi’s dimensions according to the ratio of an MG92B μservo to Rofi’s servo.
- In accordance with customer specifications, the μBiPed shall be controlled by Bluetooth on an Android phone app.
- Based on evolving needs, the payloads shall be determined by the customer.