Spring 2017 Velociraptor: DC Motor Selection
Authors
By: Mohammar Mairena (Electronics & Control)
Approved By: Jesus Enriquez (Project Manager)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Through research on DC Motors, I came across gear motors. Gear motors add mechanical gears (gearbox) to reduce speed/increase torque and vice-versa. The increase in torque is inversely proportional to the reduction in speed. Each gearmotor has a different gear ratio that alters the torque/speed calculations. Through the E&C division manager and Professor Hill, I borrowed what were said to be two GM 7’s and a GM17.
Requirement:
L2EC – 4: The velociraptor shall use DC motor(s) to drive the legs of the Velociraptor
Selecting the DC Motors
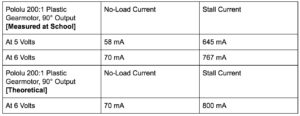
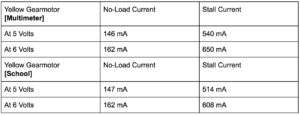
After testing what was supposed to be two GM 7’s, I realized the current values did not match up to those on the GM 7 datasheet. Upon further research, one of the GM 7’s turned out to be the pololu 200:1 plastic gearmotor with a 90° Output. The other motor was also not a GM 7 as it drew much more current than a GM 7. For both motors, I measured two things: stall current and the free running current at no-load. The stall current is the current at which the shaft of the motor is no longer rotating (under max torque conditions).
Comparing both motors, it is clear that the Pololu is much more ideal for our robot due to the low current draw it will have in comparison to the other yellow motor. In addition, it is important to note that the current draw from the Servo motors has not been taken into account. The Pololu gear motor is a great alternative to the GM 7 for 2 reasons: low current draw and high torque output.
Table 1: Pololu 200 Results
Table 2: Yellow Gear Motor Results
Resources
1) https://www.pololu.com/product/1120/specs
2) http://www.robotshop.com/en/solarbotics-gm7-gear-motor-7.html