Spring 2018 AT-ST Theo Jansen Leg
By: Danny Pham (Manufacturing and Design Engineer)
Verified By: Intiser Kabir (Project Manager)
Approved By: Miguel Garcia (Quality Assurance)
Introduction
The Theo Jansen Leg design is a design by Theo Jansen consisting of rods connecting to each other. One of the rods in the design is a static point that holds the whole leg in place and another rod which rotates in a circular motion. By rotating this specific connector in a circular motion, the whole leg moves in a circle and creates a walking motion.
Description: The gif of the Theo Jansen leg shows the simulation of a walking motion by rotating a connector in a circular motion.
The reason the Theo Jansen Leg works well with motors is because the connector spins in a circle similar to a motor. One way to look at this is spinning a crank wheel. If you attach a motor to the connector, the motor will spin that connector in a circular motion and create the walking motion for the leg. The motor is essentially turning a crank wheel that allows the rest of the leg to simulate the walking motion. A servo would not work with this design because servos only turn 180 degrees. A motor can spin this continuously and allow the leg design to walk forward without any interruptions.
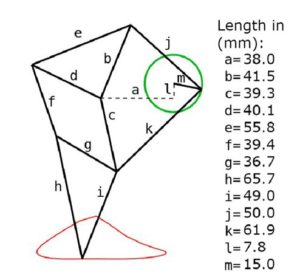
Description: These measurements are used by Theo Jansen for his leg design. The green circle represents the connector spinning in the circular motion or the crank wheel. The red line represents the circular motion that the leg moves in to create the walking motion.
One main issue to look out for using this design is controlling how the foot pivots on the ground while walking. Keeping the foot parallel to the ground is essential in order to have stability in the leg while walking. If the foot is not parallel to the ground when it is in contact with the ground, the motion is disrupted by the angle of the connector next to the foot. This will disrupt the stability of the leg and cause the leg to fall over or not walk at all.
Conclusion
The Theo Jansen leg design works well with motors. This leg design will work with our requirement of moving the legs of our robot with motors. The main priority for this design to function with our robot is having stability while the motor is running the leg. The parallel foot to the ground is essential for keeping the leg motion smooth and stable.